|
Subtypes |
Description |
Examples |
| DNA Viruses |
Herpesviruses |
DNA viruses with a complex structure causing various diseases including cold sores, chickenpox, and mononucleosis. |
HSV-1, HSV-2, VZV, EBV |
| Papillomaviruses |
DNA viruses associated with warts and certain cancers. |
HPV |
| Adenoviruses |
DNA viruses causing a wide range of infections in humans. |
Adenovirus types causing respiratory, gastrointestinal, and ocular infections |
| Poxviruses |
Large, complex DNA viruses responsible for diseases like smallpox. |
Variola virus (smallpox), Vaccinia virus |
| RNA Viruses |
Positive-Sense RNA Viruses |
RNA viruses with genomes that can directly serve as mRNA, causing diseases like the common cold, Zika, and COVID-19. |
Picornaviruses, Flaviviruses, Coronaviruses |
| Negative-Sense RNA Viruses |
RNA viruses requiring transcription into positive-sense RNA before translation, causing diseases like influenza and rabies. |
Orthomyxoviruses, Paramyxoviruses, Rhabdoviruses |
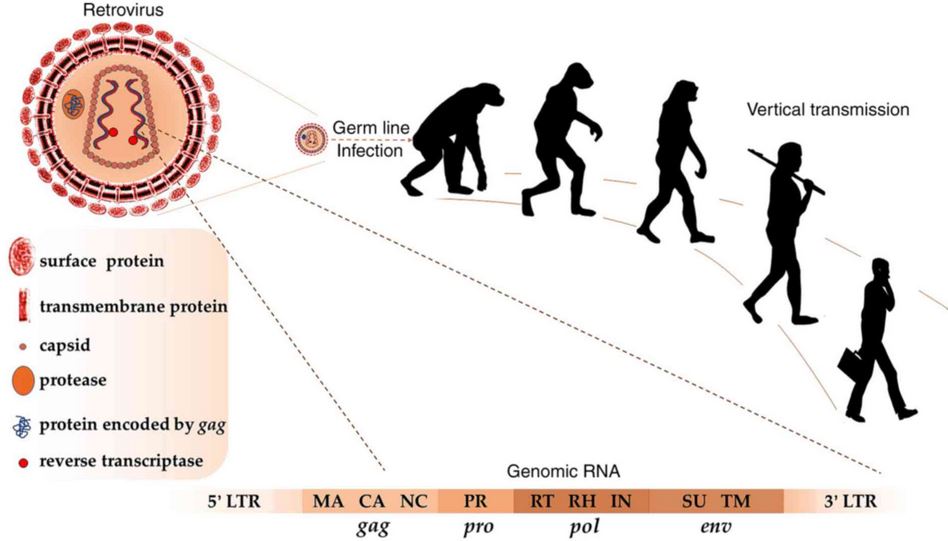
| Retroviruses |
RNA viruses that use reverse transcriptase to integrate their genome into the host cell’s DNA. |
HIV, HTLV |
| Double-Stranded RNA (dsRNA) Viruses |
RNA viruses with double-stranded RNA genomes causing gastroenteritis and other infections. |
Reoviruses |
| Single-Stranded RNA (ssRNA) Viruses with Ambisense Genome |
RNA viruses with genomes containing both positive-sense and negative-sense RNA regions. |
Arenaviruses, Bunyaviruses |
| Single-Stranded RNA (ssRNA) Viruses with Segmented Genome |
RNA viruses with genomes consisting of multiple segments, causing diseases like influenza and hemorrhagic fevers. |
Orthomyxoviruses, Bunyaviruses |
| Single-Stranded RNA (ssRNA) Viruses with Circular Genome |
Satellite viruses with a circular RNA genome requiring helper viruses for replication. |
Hepatitis Delta Virus (HDV) |
| Enveloped Viruses |
Influenza Viruses |
RNA viruses surrounded by a lipid envelope causing seasonal flu outbreaks. |
Influenza A, B, C viruses |
| Herpesviruses |
Enveloped DNA viruses causing diseases like cold sores, chickenpox, and mononucleosis. |
HSV-1, HSV-2, VZV, CMV |
| Coronaviruses |
Enveloped RNA viruses causing diseases like severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and COVID-19. |
SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2 |
| HIV |
Enveloped retroviruses responsible for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). |
Human immunodeficiency virus |
| Ebola Virus |
Enveloped RNA virus causing severe hemorrhagic fever in humans. |
Ebola virus |
| Non-enveloped Viruses |
Adenoviruses |
DNA viruses lacking a lipid envelope, causing various infections in humans. |
Adenovirus types causing respiratory, gastrointestinal, and ocular infections |
| Papillomaviruses |
DNA viruses associated with warts and certain cancers, lacking an envelope. |
HPV |
| Noroviruses |
RNA viruses causing gastroenteritis, lacking an envelope. |
Norovirus |
| Rotaviruses |
RNA viruses causing severe gastroenteritis in infants and young children, lacking an envelope. |
Rotavirus |
| Bacteriophages |
T4 Bacteriophage |
Viruses that infect bacteria, with a complex structure and lifecycle. |
T4 bacteriophage |
| Lambda Phage |
Temperate bacteriophage capable of lysogenic and lytic cycles in E. coli. |
Lambda phage |