Why in the News?
Two wetlands in Bihar, Nagi and Nakti bird sanctuaries, have been added to the global list of wetlands of international importance under the “Ramsar Convention”, bringing India’s total Ramsar sites to 82.
Do you know?
|
About Nagi-Nakti Wetland
- These wetlands, situated in Bihar’s Jamui district within the Jhajha forest range, are man-made reservoirs nestled amid dry deciduous forests and hills.
- Both sanctuaries were developed as man-made reservoirs, primarily for irrigation purposes, through the construction of dams.
- These wetlands host a diverse range of flora and fauna, including over 150 species of birds, mammals, fish, aquatic plants, reptiles, and amphibians.
Nakti Bird Sanctuary:
Nagi Bird Sanctuary:
|
Ecological Significance
- Migratory Bird Haven: The sanctuaries serve as critical wintering habitats for numerous migratory bird species, attracting over 20,000 birds during the winter months.
- Species Diversity: Nagi and Nakti sanctuaries support a rich biodiversity, including over 75 bird species, 33 fish species, and 12 aquatic plant species.
- Bar-headed Geese Congregation: Notably, the wetlands host one of the largest gatherings of bar-headed geese on the Indo-Gangetic plain, highlighting their importance as migratory bird habitats.
Back2Basics: Ramsar Convention
| Explanation | |
| Purpose | International treaty aimed at conserving and promoting the sustainable use of wetlands. |
| Establishment | Established on February 2, 1971, in Ramsar, Iran. |
| Key Components |
|
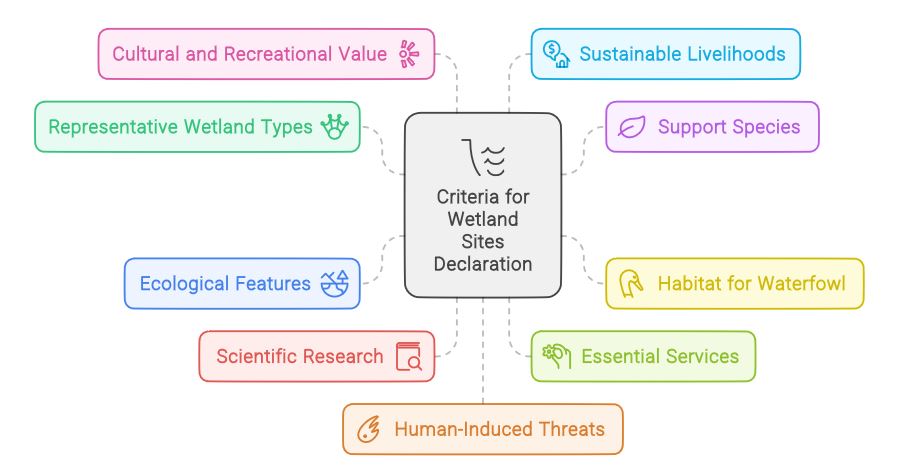
| 9 Criteria for Sites Declaration |
|
| Participating Countries | 171 contracting parties (countries) as of September 2021. |
| India and Ramsar Convention | The first Ramsar Site in India, the Chilika Lake in Odisha, was designated in 1981. |
| Ramsar Secretariat | The convention is administered by the Ramsar Secretariat, based in Gland, Switzerland. |
| World Wetlands Day |
|
| Montreux Record | Register of wetland sites on the List of Wetlands of International Importance under the Ramsar Convention that require special attention. |
PYQ:[2014] If a wetland of international importance is brought under the ‘Montreux Record’, what does it imply? (a) Changes in ecological character have occurred, are occurring or are likely to occur in the wetland as a result of human interference. (b) The country in which the wetland is located should enact a law to prohibit any human activity within five kilometres of the edge of the wetland (c) The survival of the wetland depends on the cultural practices and traditions of certain communities living in its vicinity and therefore the cultural diversity therein should not be destroyed (d) It is given the status of ‘World Heritage Site’ [2019] Consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 3 only (d) 1, 3 and 3 |