Why in the News?
The Panama Canal, which links the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans through the Isthmus of Panama, opened to ships 110 years ago. Now, it is facing a serious threat to its existence.
System of Water Elevators
- The Panama Canal utilizes a sophisticated lock system that functions as water elevators, allowing ships to navigate the elevation difference between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. This system is essential because the two oceans are at different elevations, with the Pacific being slightly higher.
Operation of the Locks
- Ship Enters: A ship approaches the first lock chamber, which is at sea level. The gate opens to allow the ship into the chamber and then closes behind it.
- Water Level Adjustment: The valve between the first and second chamber (at a higher elevation) is opened, allowing water to flow into the first chamber from the adjacent higher chamber. This increases the water level in the first chamber.
- Transition: Once the water levels between the two chambers are equalized, the gate between them opens, allowing the ship to move into the next chamber. This process is repeated until the ship reaches the desired elevation of 85 feet at Gatun Lake.
- Lowering: The reverse process occurs when lowering ships back to sea level at the other end of the canal.
| Note: Each passage requires over 50 million gallons (approximately 200 million liters) of freshwater, primarily sourced from Lake Gatun, which is vital for the canal’s operation. |
Threat of Climate Change
- Recent droughts have led to significantly lower water levels in Lake Gatun because droughts were exacerbated by climate change and the El Niño phenomenon, which have led to significantly reduced water levels in the lake.
- In 2023, rainfall was 43% lower than average, making it one of the driest years on record for the region. which reduced the number of ships able to transit the canal.
- In December, traffic dropped to as low as 22 ships per day, highlighting the vulnerability of the canal to climatic variations.
Contentious Solution
- Proposed Dam: This $1.6 billion project aims to create an additional water source for the canal on the Rio Indio, potentially securing water availability for the next 50 years. However, it has sparked controversy due to its social implications.
- Displacement Issues: The dam would flood the homes of approximately 2,000 residents, predominantly from lower socio-economic backgrounds, forcing them to relocate and lose their livelihoods. This raises significant ethical concerns regarding the balance between infrastructure needs and the rights of affected communities
Conclusion:
Before proceeding with the Rio Indio dam project, engage in thorough consultations with the affected communities, ensuring their voices are heard in the decision-making process. Need to develop a fair compensation and resettlement plan that prioritizes the socio-economic well-being of displaced residents, offering alternative livelihoods and housing options to minimize the negative impact on vulnerable populations.
Do you know about another elevation-based canal system?
- Kiel Canal (Germany): The Kiel Canal features locks that raise and lower vessels to navigate the elevation differences between the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. It is one of the busiest artificial waterways in the world.
- Welland Canal (Canada): This canal connects Lake Ontario and Lake Erie and includes a series of locks that lift ships approximately 43 meters (141 feet) to bypass Niagara Falls. It is an essential part of the Great Lakes shipping route.
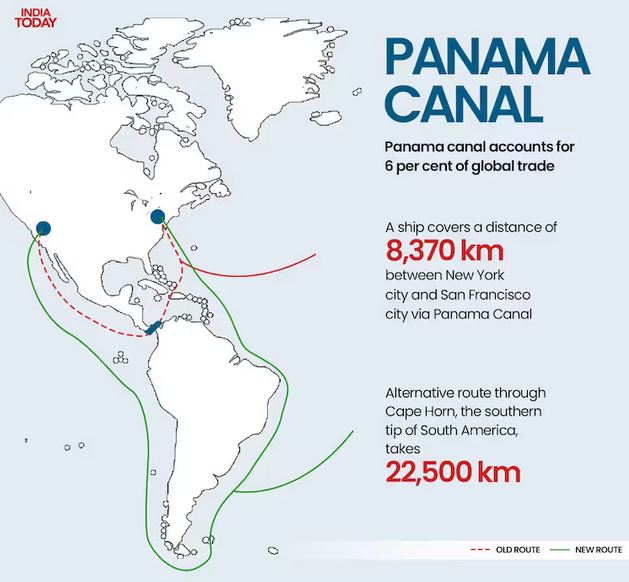
Trade from Panama Canal:
- The Panama Canal moves roughly $270 billion worth of cargo annually, which is the trade route taken by 40% of all U.S. container traffic alone. It handles about 5% of all global maritime trade.
|
Mains PYQ:
Q Mention the significance of straits and isthmus in international trade. (UPSC IAS/2022)