Why in the News?
The NGT has ordered the UP government to remove water hyacinth from “Dhanauri wetlands” and questioned its failure to designate the wetland as a Ramsar site.
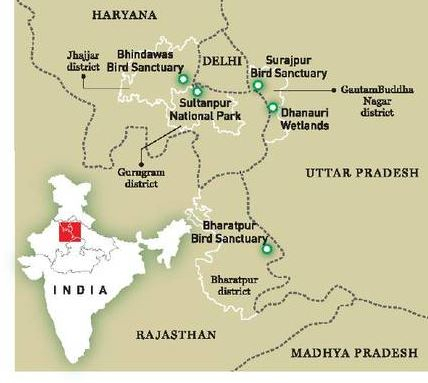
About Dhanauri Wetland
|
Details |
| Location |
- Dhanauri village near Dankaur, Uttar Pradesh;
- Floodplains of Yamuna.
|
| Key Species |
Home to over 120 Sarus Cranes (state bird of Uttar Pradesh) and 217 bird species |
| Ecological Significance |
Important birding and nesting site; recognized as an Important Bird Area by Bird Life International |
| Bird Population |
Hosts over 50,000 waterfowls during migratory seasons (November to March) |
| Ramsar Criteria |
Fulfills 2 Ramsar criteria:
1. Hosts over 1% of biogeographic Sarus Crane population
2. Congregation site for 20,000+ waterfowls |
| Conservation Status |
Documented by BNHS (Bombay Natural History Society); crucial for supporting endangered species |
Ramsar Wetlands
- The Ramsar Convention, also known as the ‘Convention on Wetlands,’ is an intergovernmental environmental treaty founded by UNESCO in 1971.
- It derives its name from the city of Ramsar in Iran, where it was initially signed.
- Ramsar sites are wetlands of global significance recognized under this treaty.
- The Montreux Record is a register of wetland sites on the brink of ecological changes and in need of close monitoring under the Ramsar Convention.
Ramsar Site Designation Criteria:
Ramsar site designation hinges on several factors:
- Representing rare or unique natural wetland types.
- Supporting endangered species or threatened ecological communities.
- Maintaining biodiversity in specific biogeographic regions.
- Offering refuge during adverse conditions.
- Regularly accommodating 20,000 or more waterbirds.
- Sustaining 1% of a population of a single water-bird species.
- Serving as a critical source of food, spawning grounds, nurseries, and migration paths for fish.
- Regularly supporting 1% of a population of non-avian wetland-dependent animal species.
|


